Aussies plan increase in military hardware expenditures

Australia releases weapons wish list amid defense spending boost
By: Nigel Pittaway
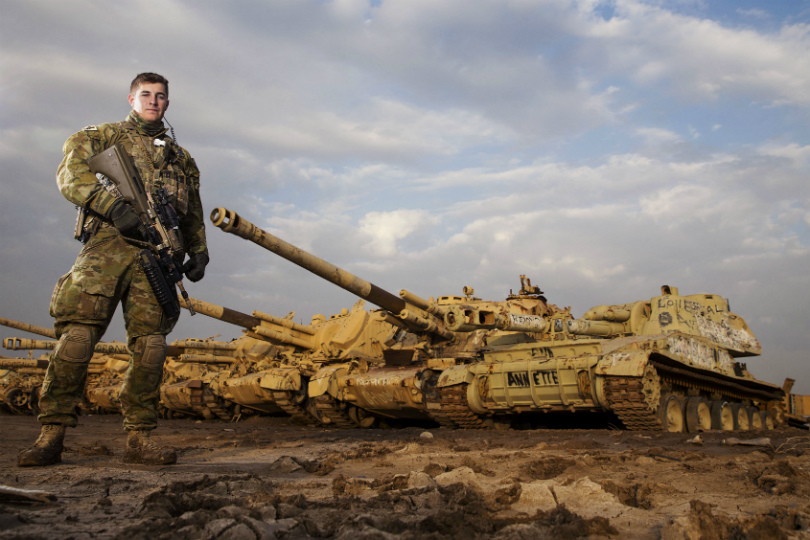
The Royal Australian Air Force Super Hornet will be the first platform to be integrated with the AGM-158C long-range anti-ship missile that the country plans to acquire. (Nigel Pittaway/Staff)
MELBOURNE, Australia — Australia plans to increase defense spending over the next decade to AU$270 billion (U.S. $187 billion) in response to what it says is a deteriorating regional environment.
The July 1 announcement by Prime Minister Scott Morrison about the plan coincides with the launch of the government’s 2020 Defence Strategic Update and the associated Force Structure Plan, which will raise projected spending from AU$195 billion as laid out in the 2016 Defence White Paper.
“The simple truth is this: we need to also prepare for a post-COVID world that is poorer, that is more dangerous and that is more disorderly,” Morrison said during the documents launch at the Australian Defence Force Academy on Wednesday.

“We have not seen the conflation of global, economic and strategic uncertainty now being experienced here in Australia in our region since the existential threat we faced when the global and regional order collapsed in the 1930s and 1940s.”
Morrison also cited trends including modernization, technological disruption and the risk of state-on-state conflict as further complicating factors in the Indo-Pacific region, which he said has deteriorated more rapidly than forecast by the previous whitepaper from 2016.
“The Indo-Pacific is the epicenter of rising, strategic competition. Our region will not only shape our future; increasingly though, it is the focus of the dominant global contest of our age,” he said. “Tensions over territorial claims are rising across the Indo-Pacific region, as we have seen recently on the disputed border between India and China, and the South China Sea and the East China Sea.”
The two defense documents forecast the development of closer ties with Australia’s regional partners and with the U.S., but it also warns of the need for enhanced self-reliance, which Morrison said signals the country’s “ability and willingness” to project military power and deter actions against it.
“Relations between China and the U.S. are fractious at best as they compete for political, economic and technological supremacy. But it’s important to acknowledge that they are not the only actors of consequence. The rest of the world and Australia are not just bystanders to this,” he said. “Japan, India, the Republic of Korea, the countries of Southeast Asia, Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Vietnam and the Pacific all have agency, choices to make, parts to play, and of course so does Australia.”
Additional capabilities to those already being acquired include long-range strike weapons, area-denial systems and cyber tools — including the establishment of an offensive cyber capability.
Also included on Australia’s shopping list is the Lockheed Martin AGM-158C long-range anti-ship missile, which would become the country’s next air-launched maritime strike weapon under Project Air 3023 Phase 1. Defence Minister Linda Reynolds confirmed Thursday that Australia will acquire an unspecified number of LRASM weapons through a Foreign Military Sales deal with the U.S. Navy.
Training on the weapon is to begin in the U.S. in 2021. The missile will initially be employed by the Royal Australian Air Force’s fleet of 24 Boeing F/A-18F Super Hornet strike fighters, with an initial operational capability to follow in 2023. Reynolds said the missile will also be F-35A Aussie jets, which are also made by Lockheed.
Australia is also seeking replacement fleets for the Royal Australian Air Force’s Lockheed Martin C-130J-30 Hercules, Airbus KC-30A Multi Role Tanker Transport aircraft, Boeing E-7A Wedgetail airborne early warning and control planes and EA-18G Growler electronic attack platforms.
The country’s Jindalee Operational Radar Network is also to be expanded to cover Australia’s eastern approaches. The government is also backing the creation of a hypersonic weapons development program.
The documents also call for the Royal Australian Navy to receive two new multipurpose sealift and replenishment vessels and up to eight mine countermeasures and tactical hydrographic vessels, to be based on the Arafura-class offshore patrol vessels now under construction in local shipyards.
The Australian  Army is to receive an active protection system for its Hawkei and Bushmaster fleets of protected mobility vehicles; two regiments of self-propelled howitzers, to be built locally; and a replacement for its Abrams M1A1 main battle tanks.
Army is to receive an active protection system for its Hawkei and Bushmaster fleets of protected mobility vehicles; two regiments of self-propelled howitzers, to be built locally; and a replacement for its Abrams M1A1 main battle tanks.
- Previous Turkey plans to return Hagia Sophia museum in Istanbul mosque status after 80 years: Greeks thinks it should not
- Next To deposit or not to deposit: British Bank’s prestiges at stake as Britain withholds Venezuelan gold