Af-Pak animosity and low intensity war – unpassable obstacle for Central Asia-South Asia transit
A round of peace talks between Pakistan and Afghanistan in Istanbul came under strain after another clash between the two countries along their border. A resolution to the conflict is important to Central Asian countries that want to trade south through Afghanistan and onward to Pakistani seaports that open the way to the Indian Ocean.
Pakistan’s government and the ruling Taliban in Afghanistan accused each other of instigating the latest confrontation on Thursday, though they still expressed commitment to a delicate ceasefire that was agreed to last month. Dozens of people were killed and cross-border trade was suspended during the fighting in October.
According to the Taliban’s account, Pakistani forces fired on the Afghan border town of Spin Boldak as the talks in Turkey began on Thursday.
Afghan forces, “out of respect for the negotiation team and to prevent civilian casualties, have so far shown no reaction. It is worth noting that in the previous round of negotiations, both sides had agreed to extend the ceasefire and prevent any acts of aggression,” Taliban spokesman Zabihullah Mujahid said on X.

Pakistan’s Ministry of Information and Broadcasting, however, said firing started from the Afghan side and that Pakistan forces responded.
“The situation was brought under control due to responsible action by Pakistani forces and the ceasefire remains intact. Pakistan remains committed to ongoing dialogue and expects reciprocity from Afghan authorities,” the ministry said.
Turkey, which along with Qatar is mediating, said ahead of the talks this week that the two sides had agreed to continue the ceasefire and establish “a monitoring and verification mechanism” to ensure peace and impose penalties for any violations. But Pakistani Information Minister Attaullah Tarar, while thanking the mediators, said late Friday that Afghanistan had failed to control terrorism, indicating that the talks in Istanbul had not overcome major sticking points.
A key dispute is over Pakistani allegations that militants have used Afghan territory as a sanctuary while carrying out attacks against targets in Pakistan. The Taliban in Afghanistan denies those allegations. Additionally, Afghanistan doesn’t recognize its porous, 2,600-kilometer border with Pakistan, saying it’s a British colonial-era construct that divided the ethnic Pashtun populations that have traditionally dominated Afghanistan.

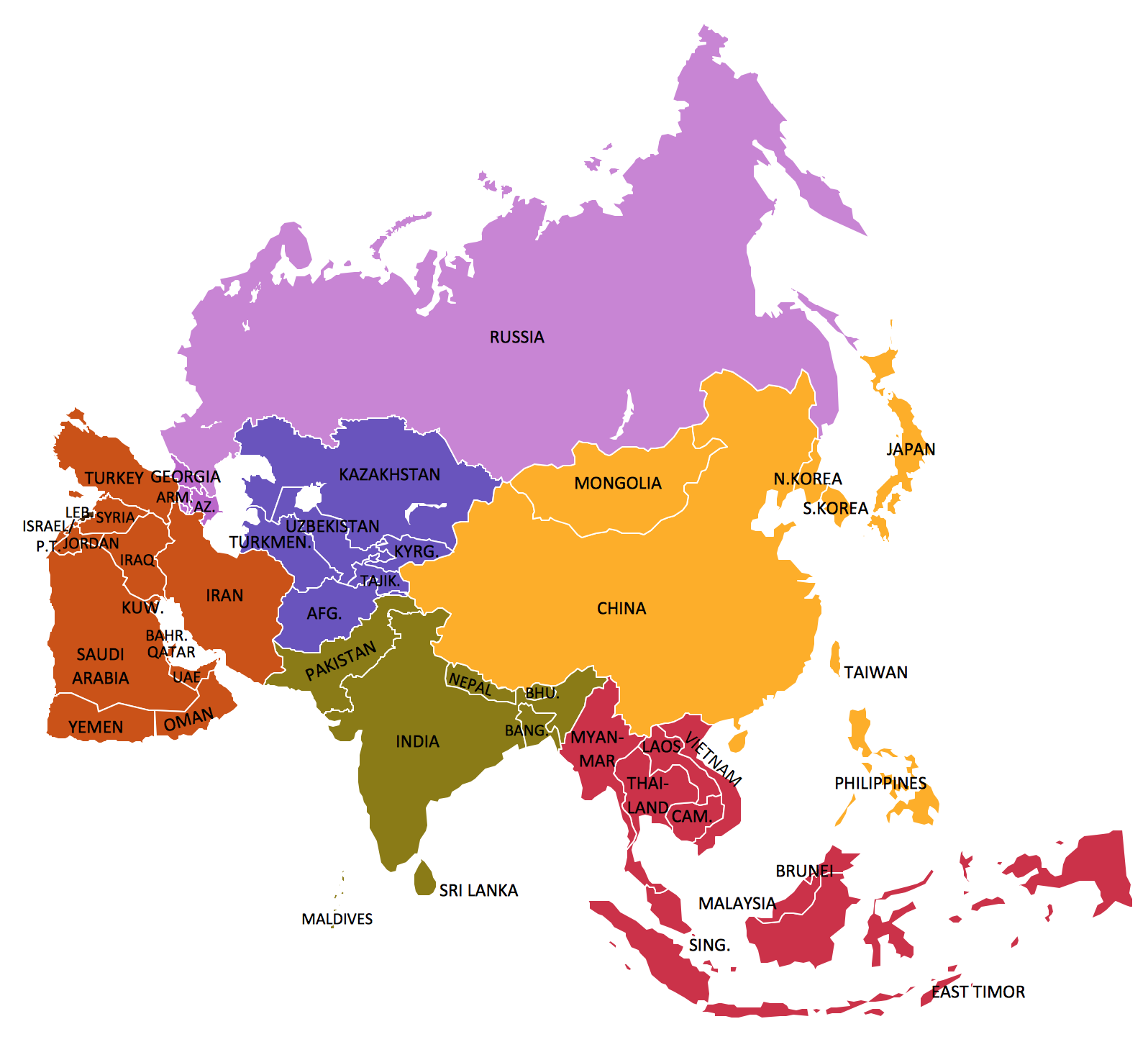
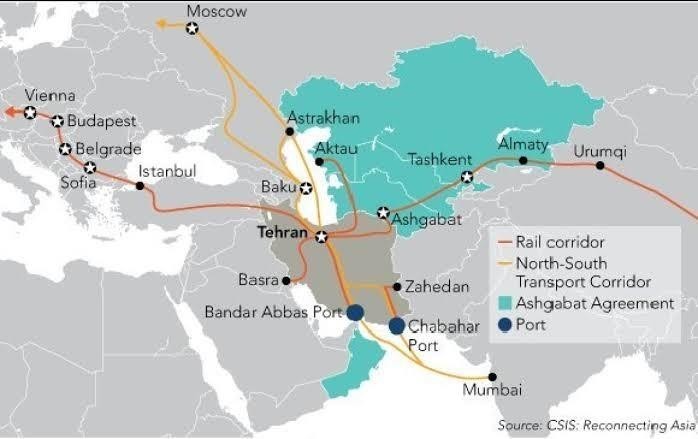
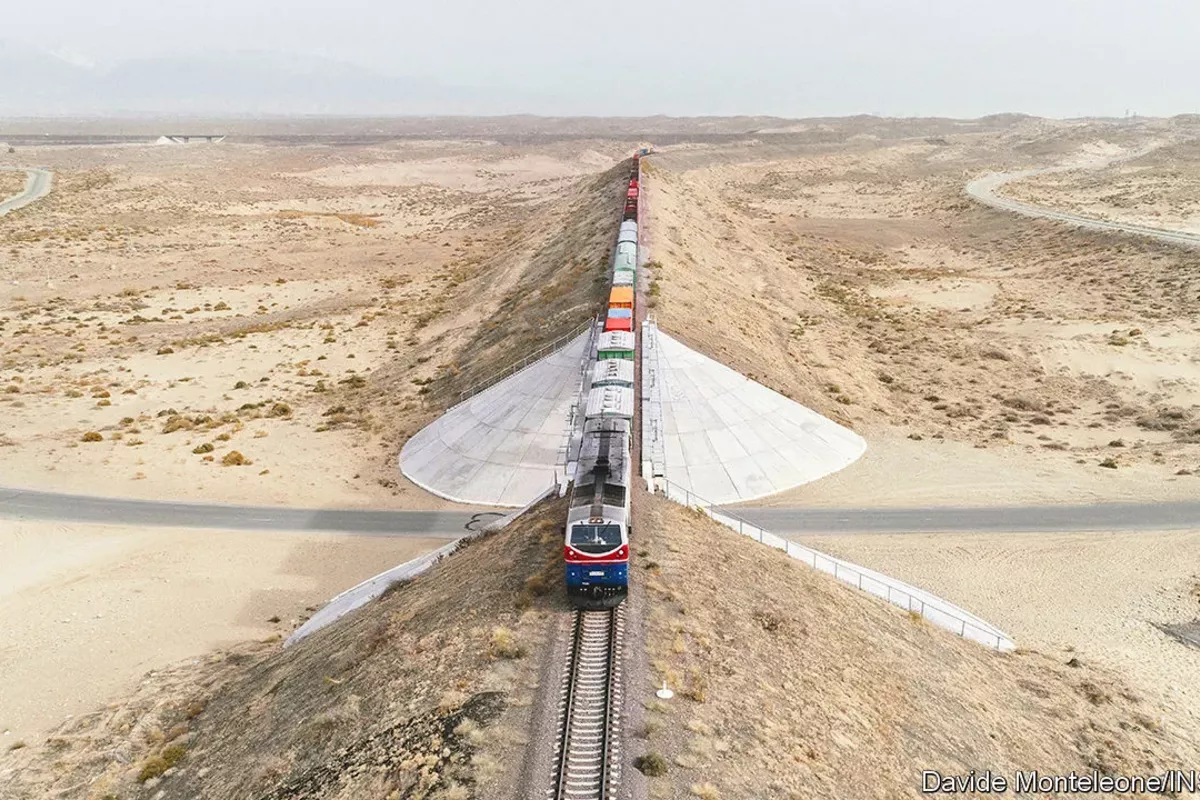
These complexities pose a challenge for landlocked countries in Central Asia that are looking to diversity their trade routes. Several Central Asia-South Asia projects in the works – the Trans-Afghan Railway, the TAPI natural gas pipeline and the CASA-1000 electricity project – have a long way to go before completion.
Meanwhile, the post-Soviet states of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan and Tajikistan are working on other trade and investment opportunities. Their leaders held a summit with U.S. President Donald Trump in Washington on Thursday, building ties with the West even as they nurture more established contacts with Russia and China.
- Previous US Commerce Secretary Howard Lutnick is Happy with Economic Agreements with Central Asia at C5+1 Summit
- Next President Trump gives sanctions exemption to PM Orban to buy Russian oil and gas, build nuclear power plant