China’s New Tool for Social Control: A Credit Rating for Everything
HANGZHOU, China—Swiping her son’s half-fare student card through the turnstile here one Monday afternoon, Chen Li earned herself a $6 fine and a reprimand from a subway-station inspector for not paying the adult fare.
A notice on a post nearby suggested more-dire consequences. It warned that infractors could be docked points in the city’s “personal credit information system.” A decline in Ms. Chen’s credit score, according to official pronouncements, could affect her daily life, including securing loans, jobs and her son’s school admission.
“I’m sure if it comes up, I can explain,“ Ms. Chen said, saying she picked up the card accidentally. “It was unintentional.”
Hangzhou’s local government is piloting a “social credit” system the Communist Party has said it wants to roll out nationwide by 2020, a digital reboot of the methods of social control the regime uses to avert threats to its legitimacy.
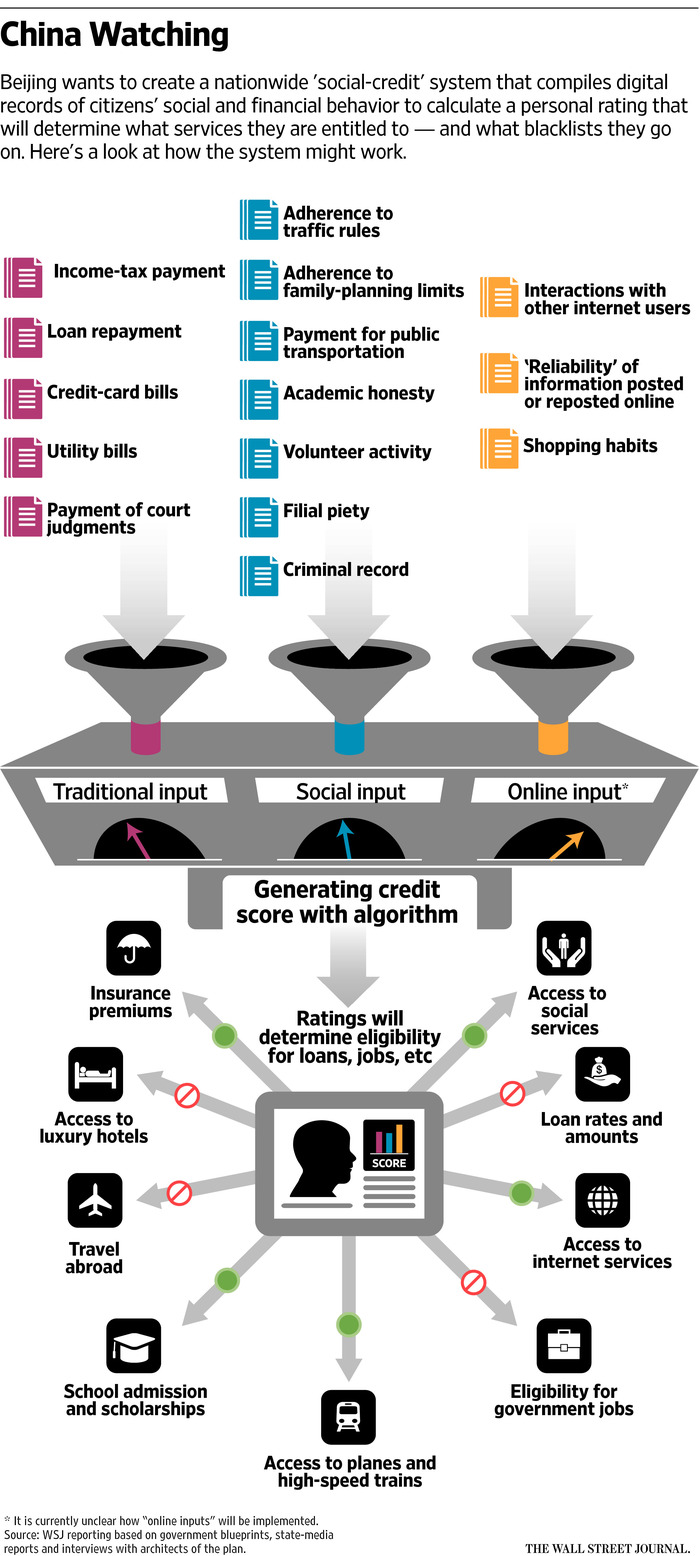
More than three dozen local governments across China are beginning to compile digital records of social and financial behavior to rate creditworthiness. A person can incur black marks for infractions such as fare cheating, jaywalking and violating family-planning rules. The effort echoes the dang’an, a system of dossiers the Communist party keeps on urban workers’ behavior.
In time, Beijing expects to draw on bigger, combined data pools, including a person’s internet activity, according to interviews with some architects of the system and a review of government documents. Algorithms would use a range of data to calculate a citizen’s rating, which would then be used to determine all manner of activities, such as who gets loans, or faster treatment at government offices or access to luxury hotels.
The endeavor reinforces President Xi Jinping’s campaign to tighten his grip on the country and dictate morality at a time of economic uncertainty that threatens to undermine the party. Mr. Xi in October called for innovation in “social governance” that would “heighten the capacity to forecast and prevent all manner of risks.”
The national social-credit system’s aim, according to a slogan repeated in planning documents, is to “allow the trustworthy to roam everywhere under heaven while making it hard for the discredited to take a single step.”
Thus far, the pilot data-collecting systems aren’t yet tied together into what Beijing envisions as a sweeping system, which would assign each citizen a rating. It isn’t clear that Ms. Chen’s ticket infraction made it into any central system, although the notice warned that fare-dodgers risked being marked down starting Jan. 1; a station agent said only repeat offenders are reported.

Zan Aizong, a Hangzhou human-rights activist, sees the system, once it’s fully operational, as an Orwellian exercise to keep closer tabs on a populace already lacking basic liberties such as freedom of speech. “Tracking everyone that way,” Mr. Zan said, “it’s just like ‘1984.’ ”
Blacklisted
China’s judiciary has already created a blacklisting system that would tie into the national social-credit operation. Zhuang Daohe, a Hangzhou legal scholar, cites the example of a client, part-owner of a travel company, who now can’t buy tickets for planes or high-speed trains because a Hangzhou court put him on a blacklist after he lost a dispute with a landlord.
“This has had a huge impact on the business,” said the client’s wife. “He can’t travel with clients anymore.” Added Mr. Zhuang: “What happens when it punishes the wrong person?”
Hangzhou officials didn’t respond to inquiries.
Another government system blacklists badly behaved tourists.
Driving the social-credit system are the State Council—China’s cabinet—and the central national-planning agency. A blueprint the cabinet published in 2014 stated it aimed to “build sincerity” in economic, social and political activity. It stressed the need for fair and clean government and for punishing polluting factories and bribe-takers.
Blacklists will expose offenders and restrict them from certain activities, while well-behaved citizens will earn access to “green lanes” that provide faster government services, the blueprint said. Citizens in jobs deemed sensitive—lawyers, accountants, teachers, journalists—will be subject to enhanced scrutiny, it said.
The State Council and national-planning agency didn’t respond to requests for comment.
China’s government must overcome technological and bureaucratic obstacles to build a system that can monitor 1.4 billion people. Government departments often guard their information, undermining efforts to build a unified database, and their systems often aren’t compatible, said Meng Tianguang, a political scientist at Beijing’s Tsinghua University who advises the government on applying “big data” to governance issues but isn’t directly involved in the social-credit system.
“Whether we can actually pull this off, we’re in a state of uncertainty at the moment,” Mr. Meng said. “Either way, it’s better than the traditional era,” until recently, he said, “when we had no data and policy was based on the judgment of individuals.”
The Shanghai government on an official website has identified scores of violations that can incur credit penalties in its pilot system, including falling behind on bills and breaking traffic rules. State-media reports list penalties for not being filial to one’s parents. (Under Chinese law, parents over 60 may sue children for not visiting regularly or not ensuring they have enough food.)
Penalties for low scorers will include higher barriers to obtaining loans and bans on indulgences such as luxury hotels, according to state-media reports.
The Shanghai system appears to still be in an early phase. Residents can check their social-credit records, but records reviewed by The Wall Street Journal didn’t show any nonfinancial data. Shanghai city officials didn’t respond to inquiries.
Despite official-media warnings and propaganda promoting sincerity, dozens of people interviewed in Shanghai weren’t aware of the social-credit plan. Many agreed more should be done to enforce higher moral standards, bemoaning habits such as spitting, cutting in line and being cold to strangers in need.
Research by Yang Wang, a Syracuse University expert on internet behavior, has shown Chinese internet users, accustomed to the idea of government snooping, are less concerned with online privacy than Americans. The most common word for privacy, yinsi, didn’t appear in popular Chinese dictionaries until the mid-1990s, he notes.
Behavior reports
In the tree-lined Yangjing neighborhood, subdistrict authorities maintain a database that gives a hint as to what elements of a broader social-credit system might look like. The database collects reports on locals’ behavior from residential committees, said Yuan Jianming, the head of the Yangjing Sincerity Construction Office.
Since mid-2015, the office has published a monthly “red list” of exemplary residents. Zhu Shengjun, 28, a high-school teacher, was named on a September red list. He said he didn’t know why. While he supported efforts to encourage better behavior, he hesitated at the idea of linking that with financial consequences, saying “it seems like too much of a stretch.”
The office also maintains a “gray list” of people behaving badly—throwing garbage out of windows, say—but the office hasn’t decided whether to publicize it, Mr. Yuan said.
In an area with a population of roughly 170,000, only around 120 have made Yangjing’s red list. Officials there complained to Chinese media this year that limited data sharing between departments was hampering efforts to rate people.
Businesses, too, get surveillance in pilot cities, where anyone can look up records on registered companies, though the records are sometimes incomplete. One objective: turning around what leaders see as a crippling lack of trust among citizens from decades of corruption and bare-knuckle competition.
So the social-credit system aims not just to collect data on individuals for official use, it seeks data on the behavior of businesses to analyze and show the results to consumers.
One example is food safety, a major issue since anger erupted over melamine-tainted milk powder that killed six infants in 2008. Subsequent scandals, including the sale of waste oil scooped up from gutters for reuse in restaurants, have continued to fuel mistrust.
Yangjing officials offer a solution: touch-screen displays they installed this summer in some restaurants. The screens, part of a local social-credit pilot system, offer an unusual level of transparency for China. Lit up with slogans—“Join heart to hand, be a model of sincerity” reads one—they display information about where ingredients came from and when waste oil was last picked up. Customers can watch videos on a mobile app showing chefs working, and the system displays the eatery’s health-department rating.
One recent Monday at Jujube Tree, a vegetarian restaurant, the food-safety console was partially obscured by poster board. Manager Wang Dacheng said it was because the system had erroneously downgraded the restaurant’s health rating, and local officials couldn’t fix it. “We have a lot of return customers. What if they come in and see that?” Mr. Wang said. He said he supported the system but was wary of its being applied without better controls.
Yangjing officials didn’t respond to inquiries.
For initial social-credit efforts, local officials are relying on information collected by government departments, such as court records and loan and tax data. More-extensive logging of everyday habits, such as social-media use and online shopping, lies with China’s internet companies, including e-commerce giant Alibaba Group Holding Ltd.
A credit-scoring service by Alibaba affiliate Ant Financial Services—one of eight companies approved to pilot commercial experiments with social-credit scoring—assigns ratings based on information such as when customers shop online, what they buy and what phone they use. If users opt in, the score can also consider education levels and legal records. Perks in the past for getting high marks have included express security screening at the Beijing airport, part of an Ant agreement with the airport.
“Especially for young people, your online behavior goes towards building up your online credit profile,” said Joe Tsai, Alibaba’s executive vice chairman, “and we want people to be aware of that so they know to behave themselves better.”
Alibaba shares aggregate data about online sales with China’s statistics bureau but doesn’t divulge personal data unless required to by law, for example in criminal investigations, Mr. Tsai said.
In the U.S., private concerns such as credit-reporting agencies and ride-sharing services compile certain ratings based on consumer data or reviews.
The local-government trials aren’t known to be tapping private-sector data, although the social-credit system blueprint designates internet data as a “strategic national resource” and calls for internet companies to contribute data, without getting into specifics.
Whether private and public data systems will be combined is still being hammered out, said Zhu Wei, a China University of Politics and Law scholar who has advised the government on social-credit efforts.
In an October speech screened to 1.5 million officials, Alibaba Chairman Jack Ma urged law-enforcement agencies to use internet data as a tool to identify criminals, according to posts on a Communist Party social-media feed. He didn’t mention sharing Alibaba’s user data. His comments raised eyebrows for broaching the notion that internet companies might share data with government agencies. Alibaba declined to make Mr. Ma available for comment. “We believe the application of machine learning and data analytics for the purpose of crime prevention is consistent with our core values: solving society’s problems,” the company said
In an interview Nov. 1 with state media, a deputy head of China’s central-planning agency, Lian Weiliang, noted that much of the government’s credit-related data were stuck on “isolated islands” and said a central data platform had been established to encourage information sharing. He said the platform had collected 640 million pieces of credit information from 37 central-government departments and various local governments.
The agency said the government has stopped untrustworthy people, identified by the court system, from buying airline tickets 4.9 million times.
Some advisers to the government, such as Mr. Zhu and Mr. Meng, said they were skeptical the system would meet the 2020 deadline because of the immense task of integrating data and keeping information secure.
In Hangzhou, where Ms. Chen used her son’s pass, residents can check their social-credit records at a government-services center. Records the Journal viewed showed only whether people had kept up with health-insurance and social-security payments—a far cry from the central government’s goals.
—Kersten Zhang, Alyssa Abkowitz and Qian Junya contributed to this article.
Write to Josh Chin at josh.chin@wsj.com and Gillian Wong at gillian.wong@wsj.com
- Previous Aung San Suu Kyi Calls Off Trip as Pressure Grows Over Rohingya Muslims
- Next Numbers of Japanese Elders in Workforce Soar